The Way To Prevent Calcaneal Spur
Overview
If you're feeling pain on the bottom of your foot near your heel, pain after exercise or activity, or pain first thing in the morning or after a long period of sitting, then you may have a heel spur. Heel spurs don't have a magic cure, but you can take steps to ease the pain and to eventually get rid of them.
Causes
Though this syndrome is most common in individuals 40 years or older, it can occur at any age. The following factors increase the likelihood of heel spur development. An uneven gait which applies too much pressure to certain areas of the foot. Being overweight. Wearing worn shoes or ill-fitting footwear. Job conditions that require long periods spent standing or lifting heavy objects. The normal aging process which results in a decrease in ligament elasticity.

Symptoms
If your body has created calcium build-ups in an effort to support your plantar fascia ligament, each time you step down with your foot, the heel spur is being driven into the soft, fatty tissue which lines the bottom of your heel. Heel spur sufferers experience stabbing sensations because the hard protrusion is literally being jabbed into the heel pad. If left untreated, Plantar Fasciitis and heel spurs can erode the fatty pad of the heel and cause permanent damage to the foot. Fortunately, most cases can be resolved without medications or surgeries.
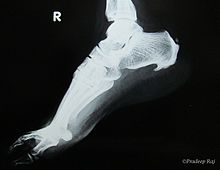
Diagnosis
Because the diagnosis of heel spurs can be confused with tarsal tunnel syndrome (as described earlier), most surgeons advocate performing a tarsal tunnel release (or at least a partial tarsal tunnel release) along with the plantar fascia release. This surgery is about 80percent successful in relieving pain in the small group of patients who do not improve with conservative treatments.
Non Surgical Treatment
FIRST, Reduce the acute pain. This is done by a combination of several things; injection of a synthetic relative of cortisone into the heel, a prescription of anti-inflammatory pills to reduce inflammation, physical therapy and a special heel pad. About 50% of the time, these treatments will permanently relieve the pain. In the other 50%, the pain becomes recurrent, and the treatment proceeds to Stage II. SECOND, Recurrent, painful heel spur is caused by the tug and pull of the plantar fascia ligament on the heel bone with each step. When the pain is recurrent, arch supports are made to prevent sagging of the arch. The arch supports are custom-made according to the size and shape of the feet. This prevents the arch from sagging and the ligament from tugging and pulling on the heel bone. The inflammation and pain eventually go away as the first phase of treatment is continued along with the arch supports, although the spur itself remains. THIRD, Surgery to remove the spur is possible and is usually done as Day Surgery.
Surgical Treatment
Have surgery if no other treatments work. Before performing surgery, doctors usually give home treatments and improved footwear about a year to work. When nothing else eases the pain, here's what you need to know about surgical options. Instep plantar fasciotomy. Doctors remove part of the plantar fascia to ease pressure on the nerves in your foot. Endoscopy. This surgery performs the same function as an instep plantar fasciotomy but uses smaller incisions so that you'll heal faster. However, endoscopy has a higher rate of nerve damage, so consider this before you opt for this option. Be prepared to wear a below-the-knee walking cast to ease the pain of surgery and to speed the healing process. These casts, or "boots," usually work better than crutches to speed up your recovery time.